GFS Policy Usage Examples
This chapter contains several basic examples of GFS retention policy usage with configuring different keeping periods for backups. With these examples, you will be able to configure the GFS policy following your business model.
GFS Yearly, Monthly, and Weekly Enabled
This example displays the keeping period assignment logic when all keeping periods are enabled in GFS settings.
Prerequisites: weekly, monthly, and yearly GFS keeping periods are enabled on April 10, 2018, with the following GFS retention settings: yearly restore points are kept for 2 years, monthly restore points are kept for 3 months and weekly restore points are kept for 2 weeks. The month of the first yearly successful backup (restore point) is April. The general retention policy settings: keep backup for one week.
The backup tree with the GFS restore point is displayed for June 25, 2019.
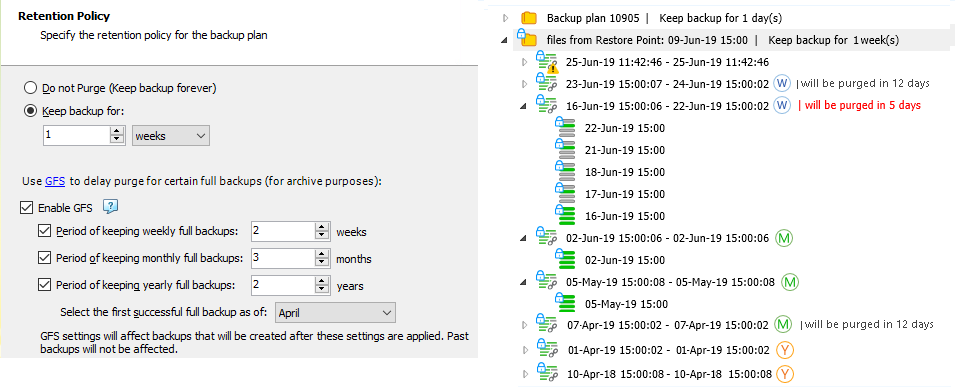
In this example, on backup storage the following restore points are kept under GFS retention:
The yearly restore point of April 10, 2018 (the first successful in the yearly period)
The yearly restore point of April 1, 2019 (the first successful in the next yearly period)
The monthly restore point of April 7, 2019 (the first successful in April 2019)
The monthly restore point of May 5, 2019 (the first successful in May 2019)
The monthly restore point of June 2, 2019 (the first successful in June 2019)
The weekly restore point of June 16, 2019 (the successful restore point on the third Sunday of June 2019)
The weekly restore point of June 23, 2019 (the successful restore point on the fourth of June, 2019)
All previous weekly and monthly restore points are already purged according to GFS policy and regular retention policy settings.
GFS Yearly and Monthly Enabled
This example displays the keeping period assignment logic when yearly and monthly keeping periods are enabled in GFS settings (weekly periods are disabled).
Prerequisites: monthly and yearly GFS keeping periods are enabled on April 10, 2018, with the following GFS retention settings: yearly restore points are kept for 2 years and monthly restore points are kept for 3 months. The month of the first yearly successful backup (restore point) is April. The general retention policy settings: keep backup for 2 weeks.
The backup tree with the GFS restore point is displayed for June 25, 2019.
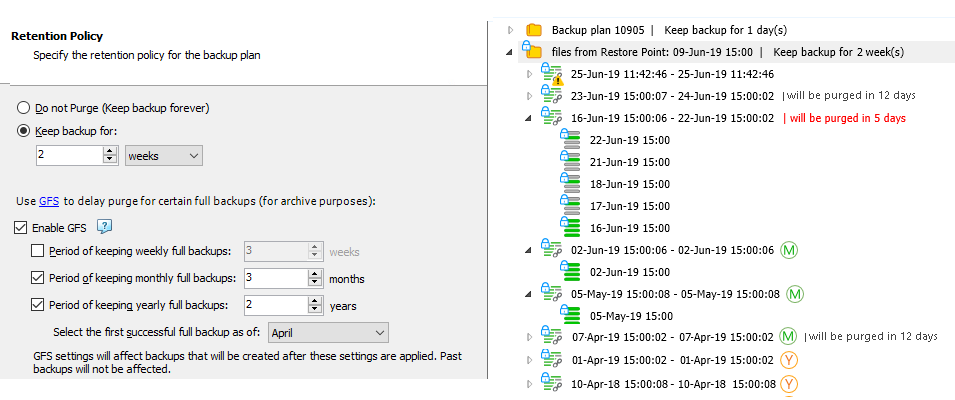
In this example, on backup storage the following restore points are kept under GFS retention:
The yearly restore point of April 10, 2018 (the first successful one in a yearly period)
The yearly restore point of April 1, 2019 (the first successful one in the next yearly period)
The monthly restore point of April 7, 2019 (the first successful one in April 2019)
The monthly restore point of May 5, 2019 (the first successful one in May 2019)
The monthly restore point of June 2, 2019 (the first successful one in June 2019)
All previous monthly restore points are already purged according to GFS policy and regular retention policy settings.
GFS Yearly and Weekly Enabled
This example displays the keeping period assignment logic when yearly and weekly keeping periods are enabled in GFS settings (monthly periods are disabled).
Prerequisites: weekly and yearly GFS keeping periods are enabled on April 10, 2018, the month of a first yearly successful backup (restore point) as of April. The general retention policy settings: keep backup for 1 week.
The backup tree with the GFS restore point is displayed for June 25, 2019.
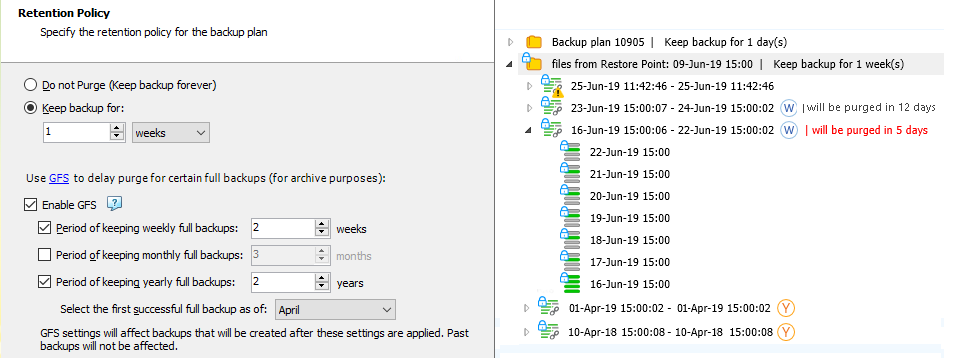
In this example, on backup storage the following restore points are kept:
The yearly restore point of April 10, 2018 (the first successful in a yearly period)
The yearly restore point of April 1, 2019 (the first successful in the next yearly period)
The weekly restore point of June 16, 2019 (successful restore point on the third Sunday of June 2019)
The weekly restore point of June 23, 2019 (successful restore point on the fourth Sunday of June 2019)
All previous weekly restore points are already purged according to GFS policy and regular retention policy settings.
A yearly restore point is kept on backup storage for a specified number of years. GFS retention period for this restore point remains the same even if GFS policy is disabled or changed.
For the yearly keeping period, full backups must be scheduled at least once a month
All previous weekly restore points are already purged according to GFS policy and regular retention policy settings.
GFS Monthly and Weekly Enabled
This example displays the keeping period assignment logic when monthly and weekly keeping periods are enabled in GFS settings (yearly periods are disabled).
Prerequisites: monthly and weekly GFS keeping periods are enabled on April 10, 2018. The general retention policy settings: keep backup for 1 week.
The backup tree with the GFS restore point is displayed for June 25, 2019.
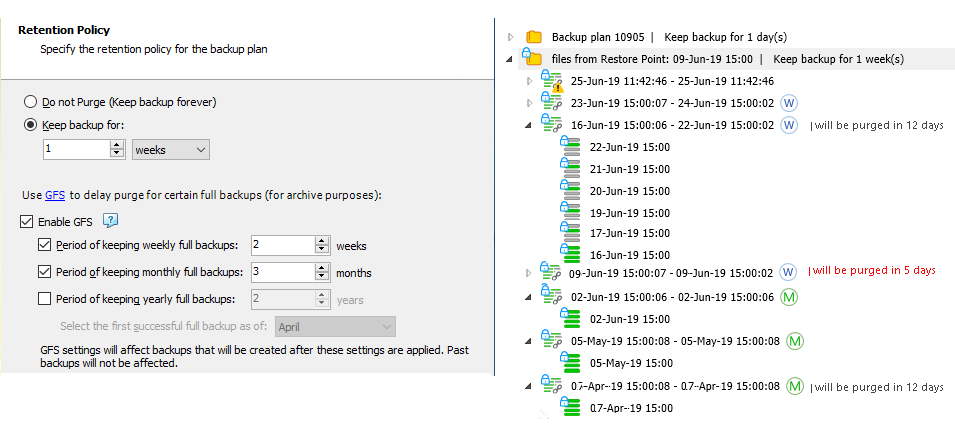
The monthly restore point of April 7, 2019 (the first successful in April 2019)
The monthly restore point of May 5, 2019 (the first successful in May 2019)
The monthly restore point of June 2, 2019 (the first successful in June 2019)
The weekly restore point of June 16, 2019 (successful restore point on the third Sunday of June 2019)
The weekly restore point of June 23, 2019 (successful restore point on the fourth of June, 2019)
All previous monthly and weekly restore points are already purged according to GFS policy and regular retention policy settings.
GFS Yearly Enabled
This example displays the keeping period assignment logic when only yearly keeping periods are enabled in GFS settings (monthly and weekly periods are disabled).
Prerequisites: yearly GFS keeping periods are enabled on April 10, 2018, with 2-year retention, the month of a first yearly successful backup (restore point) is as of April. The general retention policy settings: keep backup for 2 weeks.
The backup tree with the GFS restore point is displayed for June 25, 2019.
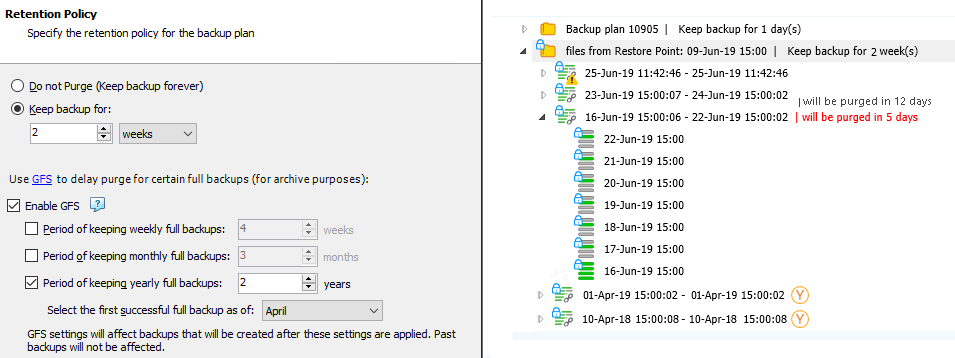
To avoid selecting the yearly restore points in a row, consider setting the current month for the yearly GFS restore point selection when you enable the GFS policy
The first successful restore point that complies with the GFS policy and with user settings (you can select the month the yearly keeping period will be selected as of) is selected as yearly.
GFS Monthly Enabled
This example displays the keeping period assignment logic when only monthly keeping periods are enabled in GFS settings (yearly and weekly periods are disabled).
Prerequisites: monthly GFS keeping periods are enabled on April 10, 2018, with 3-month retention. The general retention policy settings: keep backup for 2 weeks.
The backup tree with the GFS restore point is displayed for June 25, 2019.
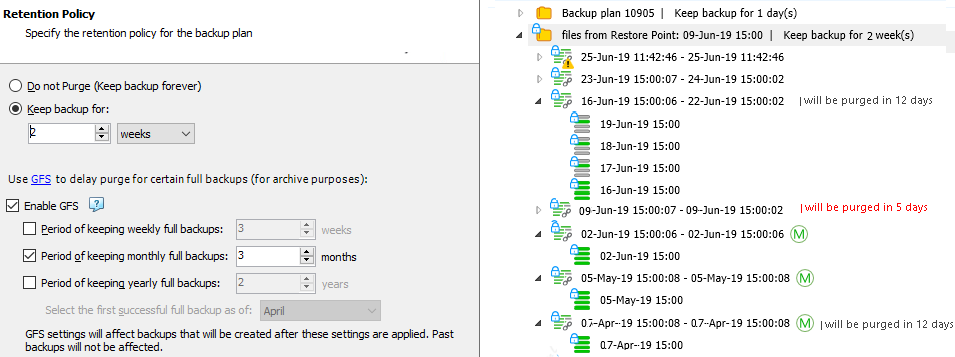
The monthly restore point of April 7, 2019 (the first successful in April 2019)
The monthly restore point of May 5, 2019 (the first successful in May 2019)
The monthly restore point of June 2, 2019 (the first successful in June 2019)
All previous monthly restore points are already purged according to GFS policy and regular retention policy settings.
For the monthly keeping period, full backups must be scheduled at least once a month
For reference, view the example of a backup tree with the same prerequisites and disabled GFS policy.
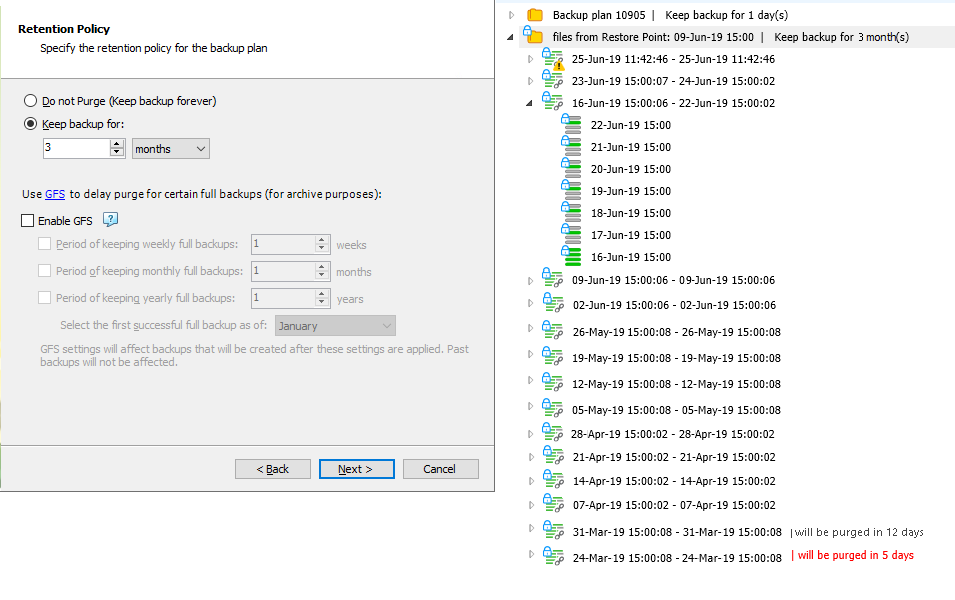
GFS Weekly Enabled
This example displays the keeping period assignment logic when only weekly keeping periods are enabled in GFS settings (yearly and monthly periods are disabled).
Prerequisites: weekly GFS keeping periods are enabled on April 10, 2018, with 4-week retention. The general retention policy settings: keep backup for 1 week.
The backup tree with the GFS restore point is displayed for June 25, 2019.
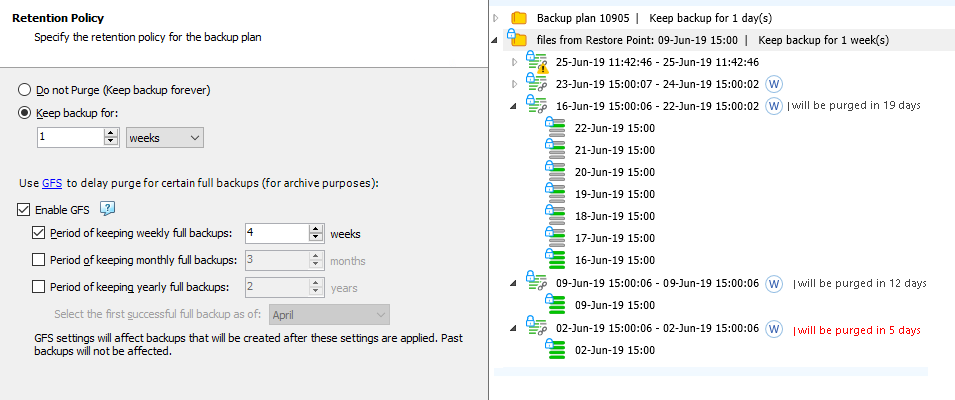
The weekly restore point of June 2, 2019 (successful restore point on the first Sunday of June 2019)
The weekly restore point of June 9, 2019 (successful restore point on the second of June, 2019)
The weekly restore point of June 16, 2019 (successful restore point on the third Sunday of June 2019)
The weekly restore point of June 23, 2019 (successful restore point on the fourth of June, 2019)
All previous weekly restore points are already purged according to GFS policy and regular retention policy settings.
For the weekly keeping period, full backups must be scheduled at least once a week
A weekly restore point is marked once a week as of Sunday.
Last updated