Retention Policy in Google Backup
A data retention policy is an agreement on retaining data for operational or regulatory compliance needs.
A data retention policy appears as a part of an overall data management and plays a significant role since the definition of the terms of keeping a company's data is crucial. Data retention on longer periods than needed produces unnecessary storage usage and increases storage costs.
If user data is modified or deleted during the retention period, a copy of the original content can be always found in the backup storage.
Objects in backup storage which retention period has expired, are deleted automatically, according to a retention policy settings, so this keeps the backup storage size under control. The duration of data retention policy can be ranged from days to years. Objects that were created/modified before the retention period starts will be skipped during backup even if these objects were included in the backup scope.
Retention policy run automatically up to 4 times a week. You can create a custom retention policy or default retention policy, that can be assigned to all users without a custom retention policy. Also you can assign a default retention policy for all users. If no default retention policy is assigned for some users, the backup data of these users will be stored forever.
Create New Retention Policy
To create a retention policy, in Account menu to the right of the horizontal menu bar click Retention Policies.
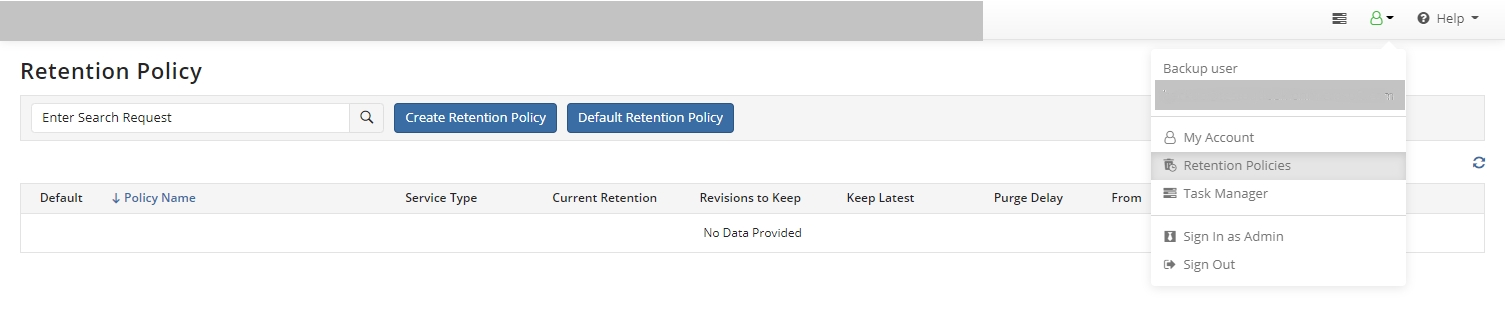
Click Create Retention Policy.
In Create Retention Policy dialog, name the retention policy.
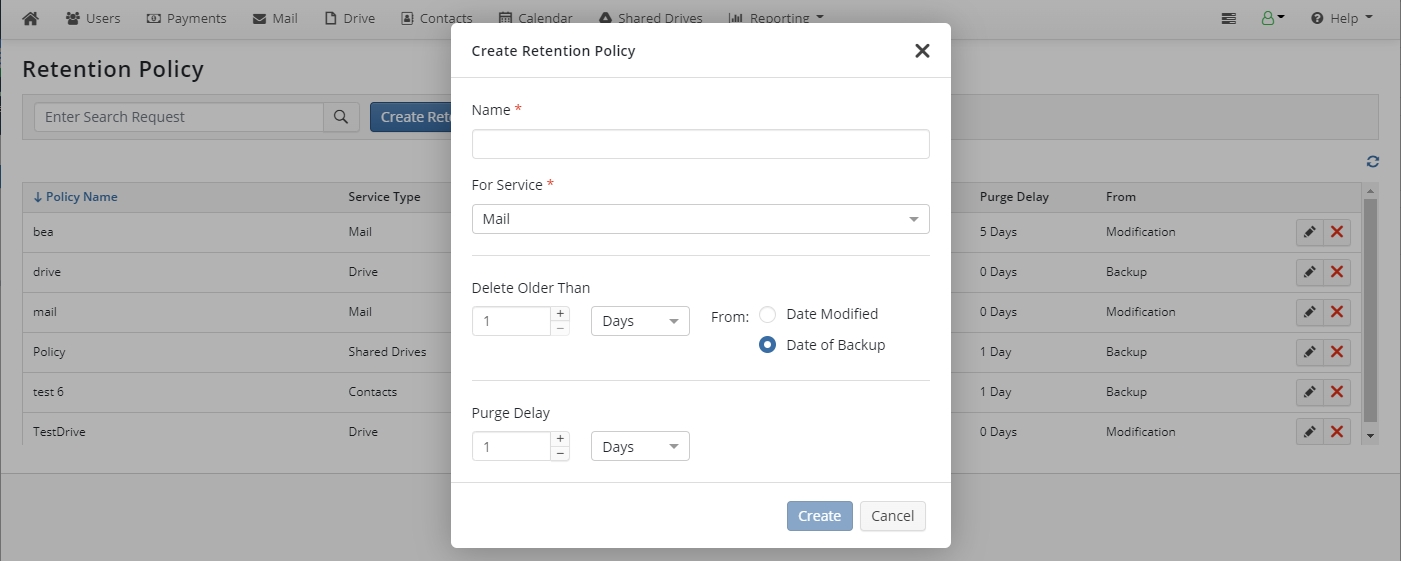
Specify the name for the new retention policy and the service the policy will be applied to.
Select backup service for which this retention policy should be applied. You can create the retention policy for the following services:
Mail
Drive
Contacts
Calendar
Shared Drives
Specify the retention policy parameters.
Delete Older Than. There are two options to retain your files. The first way is to delete all files that were modified or created before the specified date (day, week, month, and year periods are available). The second way is to delete all files that had been backed up before the specified date (day, week, month, and year periods are available).
Purge Delay. This option is an additional safety lock for your backup strategy. With this option enabled, the purging process is delayed for a specified period. Once you are done with the retention policy parameters, click Create.
Consider the following example. Let’s assume that your company requires to store all revised financial documents created less than three months ago. In this case, to ensure data is in the backup storage, select 3 months value for the Delete older than option. With this value selected, backup data will be automatically deleted from the backup storage
Once you are done with the retention policy parameters, click Create.
The new retention policy is saved and can be now assigned to selected users for the service specified in retention policy settings.
To temporarily disable the retention policy execution, select the Disable check box. The retention policy will be temporarily disabled. This does not affect other retention policies. The backup data can be still removed manually. To start this retention policy execution, clear the Disable check box.
Assign Existing Retention policy
Open the Users page, then select users the retention policy to be assigned to.
Click Retention Policy.
In the pane to the right, select the existing retention policies for all services you want.
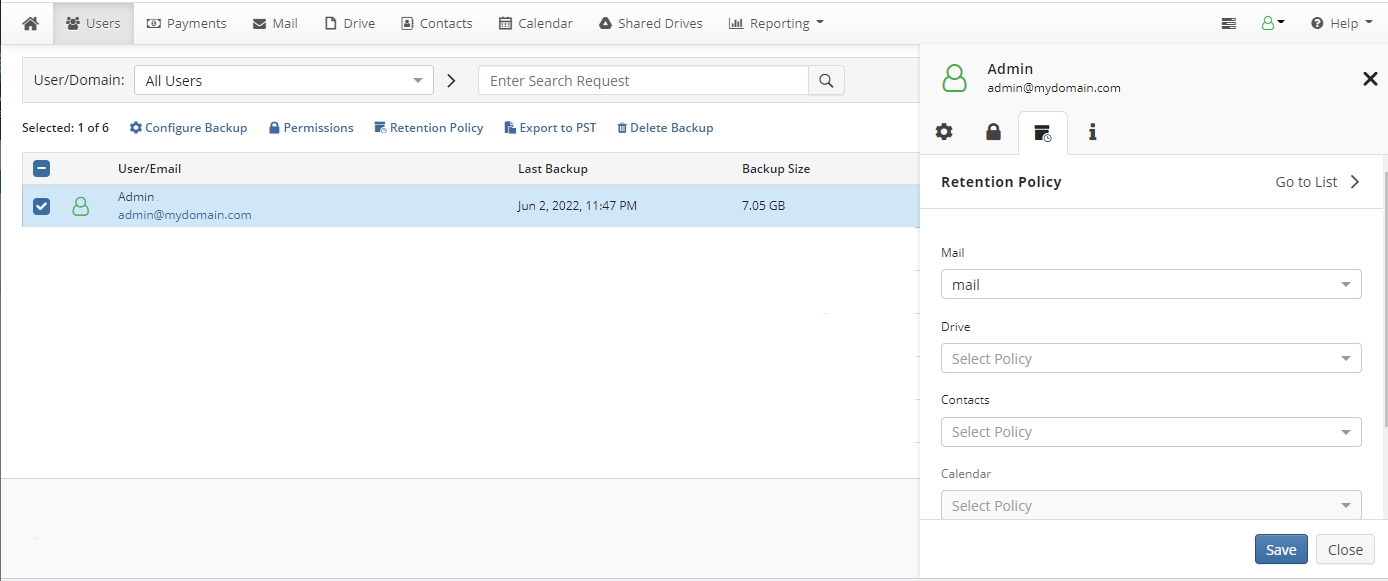
Click Save. The selected retention policies are assigned to selected users.
Configure Default Retention Policy
To create a default retention policy, in Account menu to the right of the horizontal menu bar click Retention Policies.

Click Default Retention Policy.
Select existing retention policies for the services to set them as default. This default retention policy will be applied to existing users without configured retention settings and for all new users. Users with configured retention settings will not be affected. To apply this retention policy to all users (including users with configured retention settings), select Apply to all users checkbox.
Click Save.
Edit Retention Policy
To edit a retention policy, in Account menu to the right of the horizontal menu bar click Retention Policies.
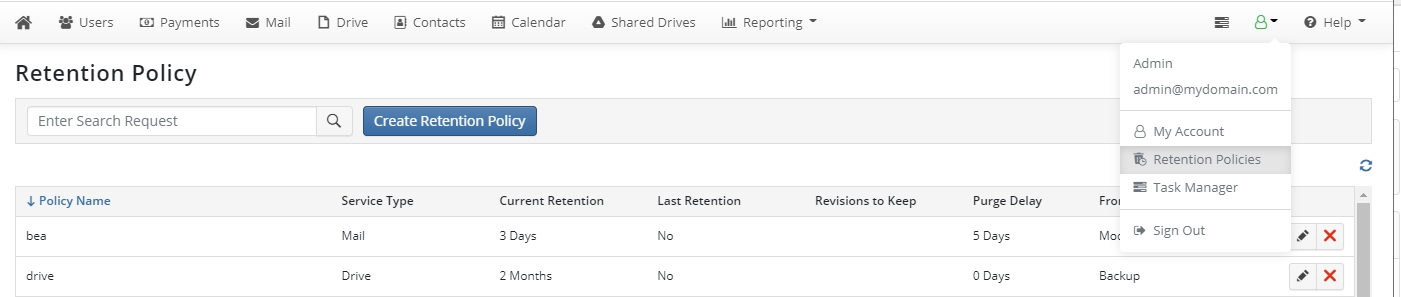
Click the retention policy you want to change, than select edit icon in actions
Once you are done with editing, click Save. Consider, if you update or change retention policies, this will initiate a full backup of the service for users to whom this retention policy was assigned.
Delete Retention Policy
To delete a retention policy, in Account menu to the right of the horizontal menu bar click Retention Policies.

Click the retention policy you want to delete, than select delete icon in actions.
Confirm the deletion of retention policy. The default retention policy will be assigned instead the deleted one. By default, your data will be stored forever.
Last updated