Application-Consistent Backups
Application-consistent backups are used to back up entities with high or extremely high transaction loads. Good examples of such entities can be Microsoft SharePoint, Active Directory, MS SQL Server, or Oracle database solutions.
When such high-transactional solutions become subject to back up, the key point is the memory state and current transactions are stopped, flushed to disk, and only then are backed up.
If memory cannot be flushed to disk for some reason, backup may not be valid for restore or some important data may be missing.
Thus, an application-consistent backup is a backup that is equipped with tools to notify applications about coming backup operation and allow applications to achieve a quiescent and consistent state by flushing all operations to disk.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Frameworks for Application-Consistent Backups
Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) is a framework designed primarily to solve the application-consistent problems for Windows operating systems. VSS is an infrastructure that provides backup applications with the feature of creating application-consistent backups.
When backup job is initiated, VSS works as follows:
Every running application that needs to flush its data kept in RAM to disk is notified by VSS.
Then a Copy-On-Write operation is performed on volume.
A volume snapshot is done and can be processed by a backup application.
VMware Application-Consistent Backups
Application-consistent backup of virtual machines on VMware environment is based on quiescence.
Note that the application-consistent backups are not supported on all guest operating systems. Read the Application-Consistent backups are unsupported in Linux virtual machine's (2044492) article at kb.vmware.com to learn a list of operating systems that support application-consistent backups
Quiescence
Quiescing is a process of bringing virtual machine file systems and application data to a consistent state. This is an important tool for correct application-consistent virtual machine backups.
To back up a currently running VM, quiescence is an efficient method. This concerns a virtual environment with highly-transactional applications (e.g. MS SQL Server or alike) since the safety of the application data is guaranteed by quiescence.
For consistent backup of virtual machines with no VSS support (Linux VMs), a crash-consistent quiescing is offered.
Also, quiescence suits to back up Microsoft Windows-based VMs with the built-in Microsoft VSS support. For these purposes, the VMware VSS component of VMware Tools is used.
To learn more, refer to Working with VSS chapter of the VMware documentation
Configure VMware Application-Consistent Backups
You can configure the application-consistent options on the Application Processing Options step of the VMware backup wizard. These options can be configured separately for each virtual machine.
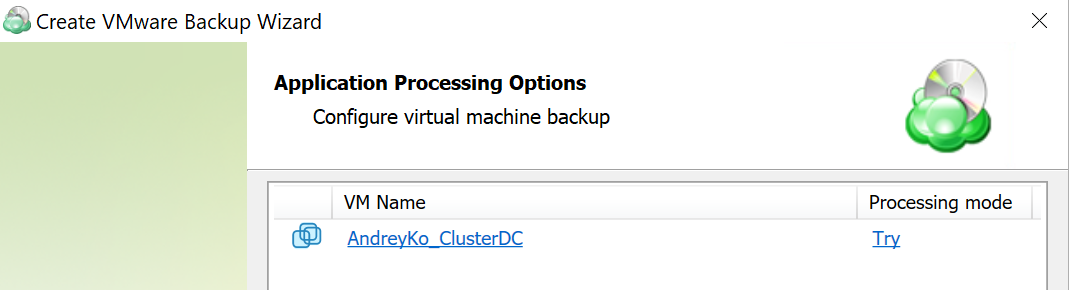
Click the application processing value to change it, if necessary.
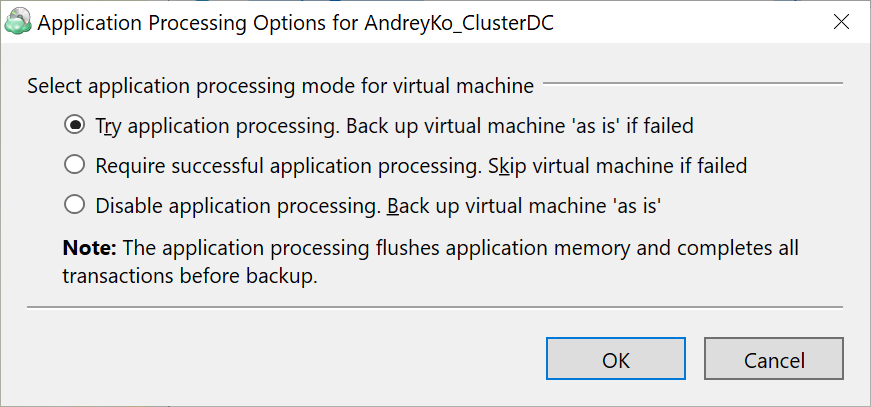
By default, the Try application processing setting is set. You can change these options separately for each virtual machine, if necessary.
The following options are available:
Try application processing. Back up virtual machines 'as is' if failed. Once this option is selected, virtual machines are backed up one by one. Using the installed VMware Tools, the state of applications running on virtual machines is checked, then a snapshot is made and an application-consistent backup is performed. In case an application-consistent snapshot is not made for some reason, a regular snapshot is done for this virtual machine.
Require successful application processing. Skip virtual machines if failed. Once this option is selected, virtual machines with applications that did not flush pending I/O operations from memory to disks, are skipped and an appropriate warning is displayed for a user.
Disable application processing. Back up virtual machines 'as is'. Once this option is selected, regular VM snapshots are done without quiescing.
Last updated